Data Types
Data types are the classification or categorization of data items. It represents the kind of value that tells what operations can be performed on a particular data.
Since everything is an object in Python programming, data types are actually classes and variables are instance (object) of these classes.
Python has the following data types built-in by default: Numeric(Integer, complex, float), Sequential(string,lists, tuples), Boolean, Set, Dictionaries, etc
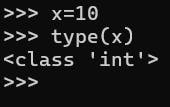
To check what is the data type of the variable used, we can simply write: your_variable=10 type(your_variable)
Data Structures
Data Structures are a way of organizing data so that it can be accessed more efficiently depending upon the situation. Data Structures are fundamentals of any programming language around which a program is built. Python helps to learn the fundamental of these data structures in a simpler way as compared to other programming languages.
Lists Python Lists are just like the arrays, declared in other languages which is an ordered collection of data. It is very flexible as the items in a list do not need to be of the same type
Tuple Python Tuple is a collection of Python objects much like a list but Tuples are immutable in nature i.e. the elements in the tuple cannot be added or removed once created. Just like a List, a Tuple can also contain elements of various types.
Dictionary Python dictionary is like hash tables in any other language with the time complexity of O(1). It is an unordered collection of data values, used to store data values like a map, which, unlike other Data Types that hold only a single value as an element, Dictionary holds the key:value pair. Key-value is provided in the dictionary to make it more optimized
Tasks
- Give the Difference between List, Tuple and set. Do Handson and put screenshots as per your understanding.
Certainly! Here's a breakdown of the differences between lists, tuples, and sets:
- List:
· Mutable: Lists are mutable, meaning their elements can be changed after creation.
· Syntax: Created using square brackets [ ].
· Order: Lists maintain the order of elements.
· Duplicate Elements: Lists allow duplicate elements.
· Example: my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4]
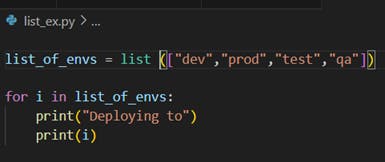
Output :

- Tuple:
· Immutable: Tuples are immutable, meaning their elements cannot be changed after creation.
· Syntax: Created using parentheses ( ).
· Order: Tuples maintain the order of elements.
· Duplicate Elements: Tuples allow duplicate elements.
· Example: my_tuple = (1, 2, 3, 4)
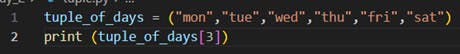
Output :

- Set:
· Mutable: Sets are mutable, but the elements contained in them must be immutable (hashable).
· Syntax: Created using curly braces { }.
· Order: Sets do not maintain the order of elements.
· Duplicate Elements: Sets do not allow duplicate elements; they automatically remove duplicates.
· Example: my_set = {1, 2, 3, 4}
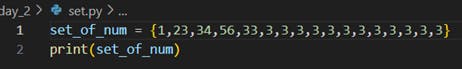
Output :
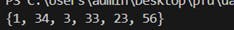
In summary, the key differences lie in mutability, syntax, order preservation, and treatment of duplicate elements. Lists and sets are mutable, while tuples are immutable. Lists and tuples maintain the order of elements, but sets do not. Lists and tuples allow duplicate elements, while sets automatically remove duplicates.
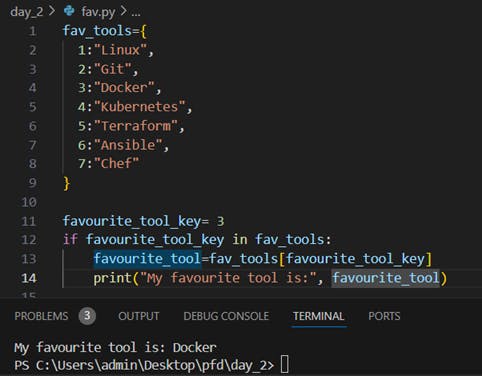
- Create below Dictionary and use Dictionary methods to print your favourite tool just by using the keys of the Dictionary.
fav_tools =
{
1:"Linux",
2:"Git",
3:"Docker",
4:"Kubernetes",
5:"Terraform",
6:"Ansible",
7:"Chef"
}
Output :
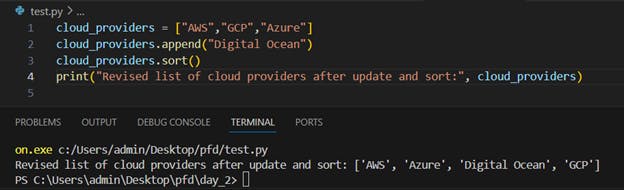
- Create a List of cloud service providers eg.
cloud_providers = ["AWS","GCP","Azure"]
Write a program to add Digital Ocean to the list of cloud_providers and sort the list in alphabetical order.
Output :
Thanks for Reading.....!!
Happy Learning....!!!!!
